
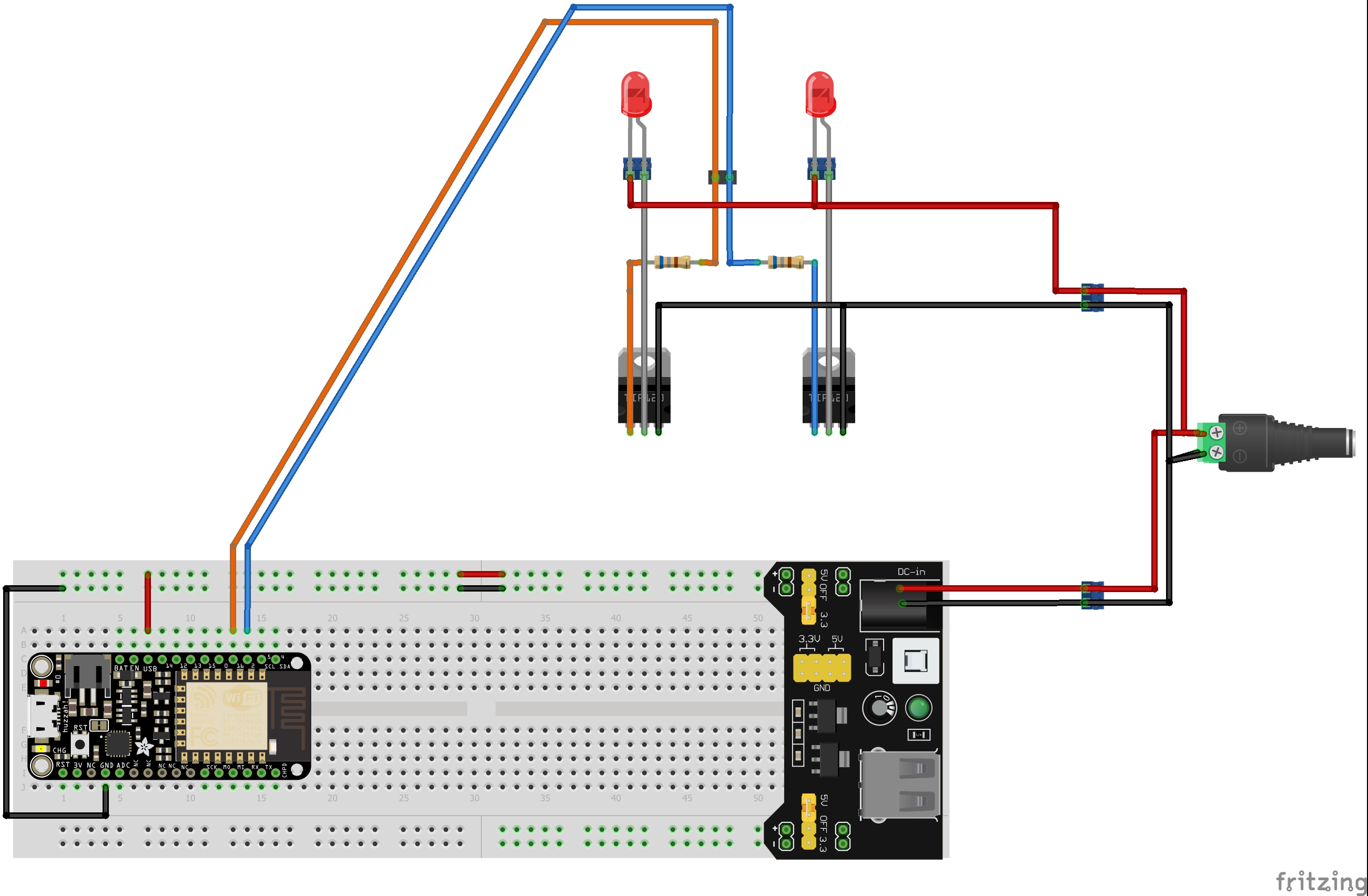
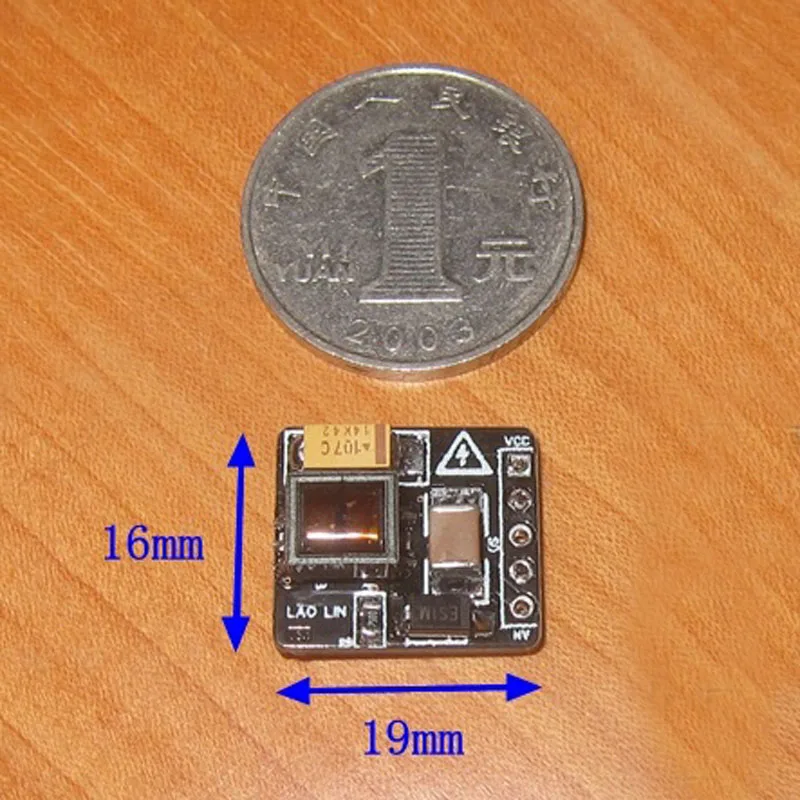
The PCB Layout was designed to be a building block component with four mounting holes, a USB micro B input connector and a terminal block output connector. Low Profile, 元 Inductor height is 10mm above PCB. Four Mounting Holes, USB-Micro B connector for the 5v input.

Nixie Tube Power Supply Schematic: Updated From Part 2 In Part 2, we will discuss the final results and experimental verification. Of course, no design is complete until you confirm with experimental results. Not counting the circuit board, the maximum component height of the proposed design is 10mm (the inductor) and the footprint size is just 14.5cm squared. In this blog, the schematic, Layout, design equations, and simulations of the design are provided. This design will operate from a 5v supply input supply, minimize the PCB footprint and use low profile and readily available parts to maximize the space available to the Nixie tubes. Most so lutions already available on the internet required a 9-16v input supply. This will allow the use of the same 5v supply used to power the Raspberry Pi, Esp8266, Arduino or other microcontroller that controls the display or IOT project. While this voltage can be made several ways, a convenient way and the subject of this blog is to generate this voltage from a 5v supply. Unfortunately, one major difficulty in using them is that Nixie tubes need voltages up to 170V to energize. The Nixie tube, invented in the 1950’s, can provide a great fusion of old display technology with new innovations.
Nixie Tubes are cool retro looking decimal digit displays useful for many modern DIY projects like the venerable Nixie tube digital clock.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
